This site is supported by our readers. We may earn a commission, at no cost to you, if you purchase through links.

The needle plunges vertically through the fabric while the feed dogs, like tiny metal paws, move the material beneath it in a steady rhythm.
Thread tension is key—it’s like Goldilocks: not too tight, not too loose. This synchronized dance of needle, bobbin, and feed dogs creates neat, durable stitches, making sewing faster and easier than ever. Curious about the mechanics behind these magic stitches? Keep reading!
Table Of Contents
- Key Takeaways
- What is a Sewing Machine?
- How Does a Sewing Machine Work?
- How Does a Sewing Machine Stitch?
- Who Invented The Sewing Machine?
- A Brief History of Sewing Machines and Clothing
- Evolution of Sewing Machines
- Double-threaded Stitching
- Stitching and Fabric Motion Synchronisation
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Conclusion
Key Takeaways
- You’ll see sewing machines use a needle and bobbin to interlock threads, creating precise stitches with perfect timing.
- Feed dogs move your fabric smoothly under the needle, keeping your stitching consistent and even.
- Thread tension balance is critical for neat, secure stitches—neither too tight nor too loose.
- Understanding thread, needle types, and machine mechanisms lets you sew efficiently with any material.
What is a Sewing Machine?
Ever wondered what makes a sewing machine tick? At its core, a sewing machine is your trusty workbench companion that joins fabrics together using a clever system of core components. Think of it as a precision instrument that’s evolved from basic functions to modern marvels of engineering.
Different machine types suit different needs – from straightforward mechanical models to computerized powerhouses packed with key features. Each one shares essential elements: a needle that pierces fabric, a bobbin that holds the lower thread, and feed dogs that guide material through smoothly.
What makes these machines special isn’t just their typical uses in crafting clothes or home décor. It’s how they’ve revolutionized the way we create, combining simple sewing machine basics with impressive capabilities. Whether you’re hemming pants or quilting an heirloom piece, understanding your machine’s mechanism is the first step to mastering this versatile tool.
How Does a Sewing Machine Work?
Your sewing machine works through a precise dance of moving parts, where the needle bar moves up and down while synchronized with the bobbin mechanism below.
The motor powers a series of gears and cams that coordinate these movements, creating perfect stitches as the feed dogs guide your fabric through.
Needle Mechanism
The needle mechanism is your sewing machine’s heart, orchestrating a precise dance with every stitch.
The needle bar moves up and down, powered by an electric motor that coordinates with internal gears. The needle’s specialized eye, designed with a groove along its shaft, carries the upper thread through your fabric. This clever design prevents the thread from getting caught as the needle pulls back up.
The needle bar mechanism plays an important role in the overall functioning of the sewing machine, allowing for efficient and smooth stitches.
Bobbin and Shuttle Mechanism
Inside your sewing machine’s heart lies the fascinating bobbins and shuttle mechanism, working like a synchronized dance team to create perfect stitches. Understanding how these components interact reveals the genius behind sewing machine mechanics:
- Your shuttle races around the bobbin case at impressive speeds – up to 1,200 rotations per minute in premium models
- Thread tension between the upper and lower threads must balance perfectly for proper stitch formation
- The shuttle hook catches the upper thread loop as it passes through your fabric
- Bobbin winding direction affects thread delivery and overall stitch quality
- Different shuttle types (oscillating, rotating, or vertical) influence sewing machine operation
To guarantee smooth operation, selecting the right sewing machine bobbin for your specific machine model is key.
This intricate system relies on precise timing between the needle’s descent and the shuttle’s movement, orchestrated by drive shafts and gears working in perfect harmony.
Feed-dog Mechanism
Modern sewing machine’s feed dog mechanism works like tiny metal teeth that grip and guide your fabric under the needle. This precise fabric feeding system guarantees consistent stitch lengths and smooth movement as you sew.
Your machine’s feed dogs rise through slots in the needle plate, moving in an elliptical pattern to advance the material. Understanding proper thread tension is essential for preventing issues like upside-down stitching and guaranteeing smooth operation of the feed dog mechanism.
| Feed Dog Types | Function | Maintenance Tips |
|---|---|---|
| Standard | Basic fabric control | Clean weekly |
| Heavy-duty | Thick materials | Oil monthly |
| Fine | Delicate fabrics | Brush after use |
| Compound | Multi-layer feed | Check alignment |
| Industrial | High-speed sewing | Daily cleaning |
Feed dog adjustment lets you control stitch regulation and fabric movement speed. When troubleshooting, check that these teeth are free from lint and properly aligned. For peak performance, regular feed dog maintenance includes cleaning between the teeth and guaranteeing smooth operation. If you’re working with delicate fabrics, consider lowering the feed dogs to prevent damage.
How Does a Sewing Machine Stitch?
A sewing machine creates perfect stitches through an intricate dance of thread interlocking between the needle and bobbin mechanism. When you start sewing, four key components work together seamlessly:
- The needle punctures the fabric while carrying the top thread, creating a precise loop underneath
- The rotating hook beneath catches this loop and guides it around the bobbin thread
- The tension balance system guarantees both threads pull equally tight, forming a secure lock-stitch
- The feed dog mechanism moves the fabric forward at just the right pace for consistent stitches
Understanding the stitch formation process is essential to appreciating how sewing machines work. This stitch formation process happens in milliseconds – faster than your eye can follow. The needle function is particularly clever: it doesn’t pass through the fabric completely like a hand sewing needle would. Instead, it creates a loop that the bobbin and shuttle mechanism catches, forming those perfectly balanced stitches you see on the surface.
Who Invented The Sewing Machine?
Elias Howe changed the course of sewing machine history in April 1845. Working as a machinist in Boston after losing his factory job during the Panic of 1837, he developed the first practical sewing machine.
This groundbreaking invention featured three key elements: a needle with an eye at the point, a shuttle beneath the cloth, and an automatic feed. Howe received U.S. Patent No. 4,750 for his innovation on September 10, 1846.
His early patents sparked a revolution in garment manufacturing. More than just a technological advancement, Howe’s sewing machine transformed society, freeing countless women from laborious hours of hand stitching. While many inventors attempted to mechanize sewing, it was Howe’s design that ultimately prevailed.
A Brief History of Sewing Machines and Clothing
The remarkable journey of sewing machines began in 1755 when Charles Wiesenthal patented the first mechanical sewing aid. Through the Industrial Revolution, hand sewing gave way to groundbreaking innovations.
Barthélemy Thimonnier’s 1829 chain-stitch machine marked a pivotal moment in early sewing history, while John Fisher’s 1844 creation combined existing innovations into the modern machine we recognize today.
These technological advancements revolutionized the garment industry, leading to cultural fashion shifts as clothing became more accessible and affordable. The development of Sewing Machines played a key role in transforming the textile industry.
The sewing machine’s invention transformed both domestic life and industrial production forever.
Evolution of Sewing Machines
From hand-cranked mechanisms to computerized marvels, sewing machine evolution mirrors our technological journey. Modern machines showcase remarkable automation advancements, transforming how we create and repair garments. Understanding the sewing machine basics is important for effective operation and maintenance.
Key innovations that shaped sewing machine history:
- Integration of electric motors replaced manual treadles, revolutionizing production speeds
- Introduction of circuit boards enabled precise stitch control and pattern memory
- Development of electronic displays simplified machine operation and settings
- Implementation of automated threading systems reduced setup time
Early sewing innovations during the industrial revolution impact sparked continuous improvements, leading to today’s sophisticated computerized sewing machines with modern features like programmable stitches and automatic tension control. These improvements build upon the initial innovations, progressing from manual operation to the computerized marvels we see today.
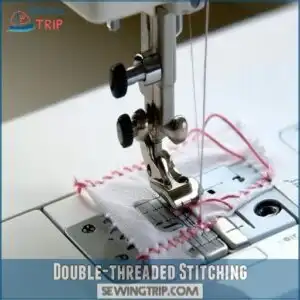
Double-threaded Stitching
Every sewing machine relies on a clever double-threaded system to create strong, lasting stitches. When you’re sewing, the needle pushes the upper thread through your fabric layers, forming a precise loop underneath.
This loop then interlocks with the bobbin thread, creating that characteristic stitch formation you see on both sides of your fabric.
Thread tension plays a key role here – when it’s perfectly balanced, your interlock stitches will be neat and secure. It’s fascinating how this simple mechanism, perfected over centuries, still forms the backbone of modern sewing machine working principles today.
Stitching and Fabric Motion Synchronisation
Creating flawless stitches is all about syncing fabric movement with sewing machine mechanics. Fabric Feed Control, feed dogs, and the rhythmic dance of loops and knots guarantee smooth sewing.
Tightening Thread Tension and using the right tools enhance precision.
| Learning Techniques | Needle Types | Foot Types |
|---|---|---|
| Tightening Thread Tension | Universal Needles | Walking Foot |
| Choosing Stitch Type | Ballpoint Needles | Zipper Foot |
| Adjusting Needle Size | Leather Point Needles | Buttonhole Foot |
Master synchronized stitch formation by understanding how these parts weave together seamlessly!
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How does a sewing machine work step by step?
Think of a sewing machine like a dance partner—precise and coordinated. You guide fabric as the needle and bobbin thread interlock stitches.
The feed dog moves fabric, while tension adjustments guarantee smooth, balanced stitching.
How did the sewing machine work?
A sewing machine works by driving a needle up and down to interlock two threads—one from the needle, the other from the bobbin—forming stitches.
Gears, pulleys, and a motor keep everything moving in sync.
How does a sewing machine move the fabric?
Over 60% of sewing issues involve fabric feeding.
Your sewing machine uses feed dogs—those tiny, tooth-like parts below the needle—to grip and pull fabric smoothly, working with the presser foot to maintain even movement.
How does a sewing machine bobbin work?
The bobbin supplies the lower thread. It rotates beneath the needle, interlocking with the top thread to form stitches.
As the sewing machine runs, the bobbin thread feeds smoothly, ensuring balanced and secure stitching.
What types of materials can be sewn with a sewing machine?
You can sew fabrics like cotton, silk, denim, and polyester.
With proper needles and settings, even delicate lace or stretchy knits are manageable.
You can also sew tougher materials like leather or canvas.
Are there any safety precautions to take when using a sewing machine?
Keep fingers clear of the needle and unplug before maintenance.
Use proper lighting and avoid loose clothing.
Don’t rush—speed leads to mistakes, and always double-check threading to prevent jams or sudden mishaps while sewing.
What are the differences between hand-sewn and machine-sewn stitches?
Hand-sewn stitches offer more flexibility and control, perfect for detailed work or repairs.
Machine-sewn stitches are faster, uniform, and stronger, ideal for larger projects or durable seams.
Both have unique strengths depending on your needs.
What is the difference between a straight stitch and a zigzag stitch?
Straight stitches are simple and linear, perfect for seams or hems.
Zigzag stitches zig and zag, offering flexibility for stretch fabrics or edge finishing. Think of zigzags as sewing’s safety net, adding strength and flair.
What is the best thread to use for a particular fabric?
For cotton fabric, use cotton thread.
For stretchy knits, go with polyester or stretch thread.
Delicate fabrics like silk need silk thread.
Denim or canvas works best with heavy-duty thread. Match strength and flexibility!
What causes sewing machine needles to bend?
Needles bend when they hit something hard like a pin, are incorrectly installed, or when the fabric is too thick.
Using the wrong needle type or size for your project can also cause bending issues.
Conclusion
Did you know the first practical sewing machine stitched up to 300 stitches per minute, revolutionizing garment-making? Today’s machines are even faster.
Seamlessly combining the needle, bobbin, and feed-dog mechanisms, these machines produce precise stitches.
Whether you’re crafting a quilt or repairing a hem, understanding how sewing machines work can boost your efficiency and confidence. Mastering thread tension, timing, and fabric movement reveals their full potential.
Ready to begin and create with expertise? Let’s get sewing!
- https://www.explainthatstuff.com/sewingmachines.html
- https://sewingmastery.com/how-often-should-a-sewing-machine-be-serviced/
- https://www.goldstartool.com/blog/what-is-the-difference-between-a-sewing-machine-and-a-serger-machine.htm
- https://home.howstuffworks.com/sewing-machine.htm
- https://sewingtrip.com/how-do-sewing-machines-work/