This site is supported by our readers. We may earn a commission, at no cost to you, if you purchase through links.

Polyester might outlast acrylic by years in outdoor gear, but acrylic’s wool-like softness makes it the go-to choice for winter wear. The catch? One releases 50% more microplastics into waterways than the other, and choosing between them means weighing durability against cost, warmth against water resistance, and immediate savings against long-term environmental consequences.
Table Of Contents
- Key Takeaways
- Polyester Basics
- Acrylic Basics
- Polyester in Insulation
- Polyester Jackets: Softshells Vs. Hardshells
- Acrylic in Insulation
- Environmental Impact
- Dangers of Washing Acrylics
- Material Costs and Chemical Resistance
- Durability and Fabrication
- Creep and Dental Applications
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Conclusion
Key Takeaways
- Polyester outperforms acrylic in durability and moisture management (absorbing only 0.4% water versus acrylic’s 4.5%), making it the superior choice for outdoor gear and athletic wear despite costing 10–15% more upfront.
- Acrylic releases approximately 1.5 times more microplastic particles than polyester per wash cycle (up to 729,000 fibers per load) and produces 134% higher greenhouse gas emissions during production, creating significantly greater environmental harm.
- While acrylic offers wool-like warmth and lower initial costs, polyester’s chemical resistance and abrasion tolerance deliver 25–30% longer service life, making it more cost-effective when you calculate total lifecycle expenses rather than just purchase price.
- The choice between these materials ultimately depends on your specific application—polyester excels in high-performance scenarios requiring water resistance and longevity, while acrylic suits cold-weather comfort items where softness and immediate affordability matter more than long-term durability.
Polyester Basics
Polyester stands out as a workhorse synthetic fiber built from polyethylene terephthalate (PET), a petroleum-based polymer created through polycondensation reactions. Its chemical composition—roughly 62.5% carbon, 4.2% hydrogen, and 33.3% oxygen—gives it noteworthy fiber properties that translate directly into performance benefits you can feel. The material’s hydrophobic nature means it absorbs less than 1% moisture, actively wicking sweat away from your skin during intense activity.
That’s why polyester production has skyrocketed to 78 million tonnes globally in 2024, dominating 57% of all fiber output. When blended with natural fibers like cotton or wool, polyester boosts durability and abrasion resistance without sacrificing breathability. Manufacturers improve this synthetic fiber further with coatings that deliver both water repellency and UV resistance—a combination that makes polyester fabric indispensable in activewear, outdoor gear, and insulation applications where material behavior matters most.
The production of polyester relies heavily on chemical resistance properties, which contribute to its widespread use in various industries.
Acrylic Basics
Acrylic fibers contain at least 85% acrylonitrile monomer units, giving them a chemical composition that’s fundamentally different from polyester’s structure. This manufacturing process relies on radical polymerization followed by wet or dry spinning—techniques that create continuous strands with densities between 1.16 and 1.18 g/cm³, making acrylic considerably lighter than wool.
You’ll appreciate acrylic fabric for its superior warmth and softness, traits that stem from porous microstructures trapping air within the fibers. The material properties include moderate tensile strength (2–4 g/d) and impressive elongation recovery—99% at 2% stretch. However, moisture regain sits at just 1.0–2.5%, explaining why breathability remains acrylic’s weakest link.
Despite this limitation, textile applications favor acrylic for cold-weather accessories, upholstery, and technical uses where hypoallergenic qualities and UV resistance outweigh ventilation concerns. The production of acrylic fabric involves a complex polymer creation process that affects its overall quality and durability.
Polyester in Insulation
Shifting from acrylonitrile chemistry to another synthetic workhorse, you’ll discover polyester’s role in insulation hinges on recycled PET and structural innovation. Thermal performance reaches R-2.0 to R-4.1 per 100 mm, delivering heat retention through thermally bonded fibers that resist compression. This thermal behavior translates to consistent warmth across roofs, walls, and floors—critical for thermal comfort in demanding climates.
Here’s what sets polyester fabric apart in insulation applications:
- Recycled PET content up to 85% slashes carbon emissions dramatically
- Non-toxic, hypoallergenic construction health safety during installation
- Zero VOC emissions and dust-free handling protect indoor air quality
- Full recyclability aids circular production and reduces landfill burden
- Market growth projections show insulation demand reaching $114.6 billion by 2033
Environmental impact remains favorable compared to virgin materials, while weaving techniques and batt construction maintain stable R-values over decades without degradation.
Polyester Jackets: Softshells Vs. Hardshells
Beyond the sphere of insulation batt and recycled PET innovation, polyester dominates the performance jacket market through two distinct constructions. Softshell jackets rely on woven polyester blends with spandex, pairing fleece-backed inner layers with DWR-treated exteriors to deliver breathability levels exceeding 15,000 g/m²/24h—ideal for high-exertion pursuits where moisture-wicking matters most.
Hardshell jackets, by contrast, employ two- to three-layer laminated polyester with membranes like Gore-Tex, achieving waterproof ratings above 20,000 mm but sacrificing breathability to roughly 8,000–10,000 g/m²/24h. Weight comparison reveals hardshells compress 25–30% smaller, enhancing packability factors for alpine expeditions, while softshells trade bulk for comfort and flexibility.
Market trends confirm recycled polyester now constitutes up to 65% of fabric input, reflecting the environmental impact consciousness driving outdoor gear evolution.
| Feature | Softshell Jackets | Hardshell Jackets |
|---|---|---|
| Waterproof Ratings | Light rain resistance (DWR coating) | 20,000+ mm (membrane sealed) |
| Breathability Levels | 15,000+ g/m²/24h | 8,000–10,000 g/m²/24h |
| Weight Comparison | 15 oz–1.6 lb (0.42–0.73 kg) | ~1 lb (0.45 kg) |
| Packability Factors | Moderate compression | 25–30% smaller pack volume |
| Primary Use | Active aerobic pursuits | Extreme weather protection |
Acrylic in Insulation
When you’re hunting for warmth without weight, thermal conductivity becomes your compass. Acrylic registers just 0.19 W/(m·K)—far below single glass at 0.80—meaning you retain heat even in lightweight sweaters and blankets that rival wool’s insulation efficiency.
That’s why manufacturers embed acrylic fibers in building coatings rated to 150 °C, capturing 31.8% of the global insulation coatings market. Moisture resistance amplifies this advantage: acrylic’s low water absorption keeps thermal comfort intact during drizzle or perspiration, while fast-drying structures prevent the clammy chill polyester sometimes harbors.
Structural applications extend from automotive interiors to aerospace panels, where durability longevity matters—flame-retardant variants retain 40.7% mass under fire, and UV-stable coatings preserve performance across decades.
Energy efficiency follows naturally; insulated acrylic panels slash heating costs by blocking heat loss through windows and walls, delivering material comparison wins where light transmission and insulation must coexist.
Environmental Impact
When you choose synthetic fabrics, you’re making a decision that ripples far beyond your closet. Both acrylic and polyester carry significant environmental costs that begin at production and continue throughout their entire lifecycle.
Understanding these impacts helps you weigh the true price of durability and affordability against the planet’s wellbeing.
Microplastics
When you wash synthetic fabrics, you’re basically releasing invisible plastic particles into waterways—a phenomenon called Fiber Shedding. Acrylic releases approximately 1.5 times more microplastic particles than polyester during each wash cycle, contributing to Water Contamination.
Consider these impacts of Microplastic pollution:
- Acrylic fabrics shed about 730,000 microfibers per wash cycle
- Wastewater treatment plants allow up to 40% of microfibers to escape into rivers and oceans
- These microfibers cause Ecological Damage by entering the food chain through plankton and fish
- Persistent microplastics introduce toxic chemicals into ecosystems, raising concerns about Human Health
The Environmental impact of synthetic fibers extends beyond what you can see. Mitigation Strategies include using front-loading machines, washing at lower temperatures, and choosing natural alternatives when possible to reduce Textile waste from Microfibers.
Not Biodegradable
Once synthetic fibers like acrylic and polyester enter landfills, they persist for over 200 years due to their remarkable Polymer Stability. You won’t find easy Decomposition Rates here—laboratory studies show only 7% mass reduction under controlled biodegradation attempts.
This Landfill Persistence creates Textile waste that generates Methane Emissions as fibers slowly degrade anaerobically.
Despite representing 60% of global fiber production, Synthetic fibers face severe Recycling Challenges, with less than 5% converted into similar-grade materials, amplifying their Environmental impact and contributing to ongoing Microplastic pollution and Biodegradability concerns.
Greenhouse Gases
When you pick acrylic over polyester, you’re choosing a fiber with acrylic emissions nearly 134% higher—releasing roughly 46,660 kg CO₂e per tonne versus polyester’s 19,920 kg CO₂e. Energy demand tells a similar story: acrylic requires 175 MJ/kg, about 40% more than polyester’s 125 MJ/kg.
These greenhouse gases and microplastic pollution drive industry impact, contributing to the fashion sector’s 944 million metric tonnes annually.
Reduction pathways exist—recycled polyester cuts emissions by 25–30%, and renewable electricity could slash process emissions by 40%, addressing environmental concerns around environmental sustainability.
Dangers of Washing Acrylics
Every time you wash an acrylic sweater or blanket, you’re sending thousands of invisible plastic threads into waterways—up to 729,000 synthetic microfibers per laundry load. Acrylic fabric sheds nearly 1.5 times more microplastic pollution than polyester fabric, making it one of the worst offenders in microfiber pollution. These particles slip through wastewater treatment plants and infiltrate aquatic ecosystems, where marine life mistakes them for food. The result? Contaminated seafood that brings microplastics back to your plate—contributing to an estimated 78,000 to 211,000 particles of human ingestion annually.
Each wash of acrylic fabric releases up to 729,000 microfibers into waterways—contaminating seafood and delivering thousands of plastic particles back to your plate
Five Mitigation Strategies You Can Use Today:
- Install washing machine filters that capture up to 89% of fiber emissions
- Use specialized laundry bags like Guppyfriend to trap 54–80% of shed fibers
- Wash acrylics in cold water and shorten cycles by 50% to reduce shedding by 30%
- Choose natural fiber alternatives when possible to minimize environmental impact of fabrics
- Follow proper fabric care and maintenance by washing synthetic garments less frequently
Material Costs and Chemical Resistance
When you’re choosing between acrylic and polyester, understanding the financial trade-offs reveals a fascinating paradox. Acrylic yarn generally costs 10–15% less per kilogram than polyester yarn, with acrylic acid pricing around US$1.01/kg in Northeast Asia compared to US$1.79/kg in North America—substantial regional variations that affect your bottom line.
However, polyester’s chemical compatibility tells a different story. It resists solvents like acetone and methyl ethyl ketone far better than acrylic, which cracks and fractures under the same exposure. This chemical resilience translates to 25–30% longer service life, making polyester’s cost-effectiveness excel over time.
While acrylic’s lower upfront cost tempts budget-conscious buyers, polyester’s chemical properties and durability reduce replacement frequency and repair expenses. Both markets are growing at roughly 5% annually, but polyester’s chemical composition—resistant to corrosion, UV degradation, and most dilute acids—justifies its premium pricing when you calculate lifecycle costs rather than just initial material expenses.
Durability and Fabrication
Polyester fabric delivers higher tensile strength and greater abrasion resistance compared to acrylic fabric, but these mechanical advantages come with fabrication trade-offs you must weigh. Polyester’s brittleness increases breakage risks during handling and creates more airborne dust when you’re sanding it—a real concern for your safety.
Acrylic fabric wins on ease of repair and fabrication methods. When you’re working with acrylic, chemical bonding for seams reduces human error versus polyester’s mechanical seaming approach. You’ll also generate less hazardous particulate during shaping, keeping your workspace safer. That’s why many fabricators prefer acrylic despite polyester’s advantage in durability.
Thermal stability affects your choices too. Acrylic’s pyrolysis temperature ranges from 190°C to 230°C, while polyester withstands higher heat during processing. However, pilling behavior tests consistently show acrylic generates more microplastics from fiber breakage—a durability concern over time.
Balance these synthetic fiber properties against your specific needs: polyester for strength-demanding applications, acrylic when fabrication ease matters most.
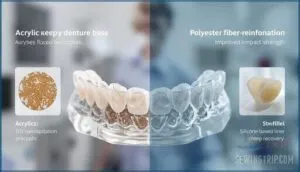
Creep and Dental Applications
When you’re selecting materials for dental prosthetics, creep—the gradual deformation under sustained load—becomes a make-or-break factor. Reinforced PMMA, the acrylic workhorse of denture bases, exhibits creep strain that increases from 1.4% to 2.4% as load doubles from 10 N to 20 N over four hours. That’s why adding TiO₂ nanoparticles cuts creep strain by 65%, dramatically improving denture base creep resistance.
Polyester fiber reinforcement offers another path: 4 mm fibers boost impact strength by 25% while reducing permanent deformation in bis-acrylic matrices. Composite creep strain ranges from 0.43% in dry conditions to 2.87% after ethanol exposure, showing how your mouth’s environment matters.
Silicone-based liners achieve 95% creep recovery versus acrylic’s 75%, directly affecting clinical implications like prosthesis fit over time. These material comparison insights help you minimize the 0.5% vertical deformation typical after one year of chewing.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How does acrylic compare to polyester for moisture management?
In moisture management, polyester absolutely dominates the field. Polyester fabric excels with excellent wicking performance and breathability factors, thanks to its hydrophobic nature—absorbing only 4% water compared to acrylic’s 5%.
Which fabric is better for outdoor furniture upholstery?
When your outdoor furniture faces relentless sun and rain, material selection matters. For UV resistance and color fastness, acrylic excels—lasting over 10 years outdoors with minimal fading. Polyester offers exceptional abrasion durability and wrinkle-resistant weaving, ideal for high-traffic areas.
Your choice depends on prioritizing weather resistance versus fabric longevity under heavy use.
Can acrylic or polyester be dyed after manufacturing?
Yes, both fabrics accept dyes post-manufacture, but through different methods. Acrylic relies on cationic dyes with dye exhaustion above 95%, while polyester uses high-temperature disperse dyeing. Each requires specific fiber treatment to achieve excellent color fastness and dye affinity.
Which fabric is more suitable for athletic wear?
When you’re pushing through a workout, fabric performance matters. Polyester dominates athletic wear thanks to its moisture-wicking properties and quick-drying capabilities.
Its exceptional durability and tensile strength handle high-stress movements better than acrylic, making it the go-to choice for activewear and sportswear materials.
How do acrylic and polyester perform in fire resistance?
When flames meet synthetic fibers, the real test isn’t just whether they catch fire—it’s what happens next. Polyester fabric ignites around 432°C and melts rather than burns, which limits flame spread but creates dripping hazards. Acrylic fabric requires higher temperatures (460-650°C) to ignite, yet both produce toxic fumes and dense smoke during combustion.
Flame retardants dramatically improve fire resistance in both materials, reducing combustion rates by nearly 50% and achieving Class A ratings through phosphorus-based treatments that promote char formation—a protective barrier that insulates against heat transfer.
Conclusion
Choosing between acrylic vs polyester is like picking between a warm hug and a weatherproof shield—each excels where the other stumbles. Polyester wins on durability and water resistance, making it ideal for outdoor gear that faces harsh conditions. Acrylic delivers wool-like softness and enhanced warmth retention for winter apparel.
Your decision hinges on priority: if longevity and moisture management matter most, polyester justifies its higher cost. If immediate comfort and affordability drive your choice, acrylic delivers. Both carry environmental baggage, so weigh performance against planetary impact before you buy.
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC11314402/
- https://textile-yarn.com/blog/the-acrylic-vs-polyester/
- https://geopelie.com/en/blogs/blog/the-environmental-impact-of-the-different-textile-fibers
- https://www.emergingtextiles.com/fiber-market-prices/fiber-market-price-comparison/
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0926669024024270